How IoT Protocols Enable Fleet Connectivity
Explains MQTT, CoAP, HTTPS and LoRaWAN and how they enable real‑time tracking, low‑power long‑range monitoring, predictive maintenance and secure fleet data.

IoT protocols are the backbone of modern fleet connectivity, ensuring vehicles, sensors, and management systems communicate efficiently. They standardise data exchange, improving transmission reliability, battery efficiency, and security. Key protocols like MQTT, CoAP, HTTPS, and LoRaWAN address different operational needs, from real-time tracking to long-range monitoring in remote areas.
- MQTT: Lightweight and ideal for real-time telemetry in urban fleets.
- CoAP: Low-power protocol suited for battery-operated sensors.
- HTTPS: Ensures secure data exchange for dashboards and APIs.
- LoRaWAN: Long-range, low-power option for rural tracking.
These protocols enable real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, and enhanced security. For instance, MQTT supports instant updates, while LoRaWAN ensures communication in areas with poor coverage. Choosing the right protocol depends on bandwidth, range, and power requirements, making them indispensable for efficient fleet management.
A Practical Guide to Industrial IoT Connectivity: Standards | Protocols Podcast Ep 04 Stan Schneider
Main IoT Protocols Used in Fleet Connectivity
IoT Protocol Comparison for Fleet Management: MQTT, CoAP, HTTPS, LoRaWAN
Fleet telematics relies on specific protocols to handle data transmission and organise information. The right protocol for your fleet depends on factors like power availability, geographic coverage, and the type of data being sent. Below, we explore key protocols and their roles in keeping fleets connected.
MQTT: Lightweight Messaging for Real-Time Tracking
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport) is widely used in connected vehicle platforms. It works on a publish-subscribe model, where vehicles transmit data to specific topics, and the fleet management system subscribes to these updates. This approach simplifies network operations and is ideal for vehicles operating with limited bandwidth. Its minimal header size is particularly effective in low-bandwidth environments.
Andrew Givens, an IoT Specialist at AWS, highlights its advantages:
"MQTT is an ideal communication protocol for connected vehicle platforms because it is lightweight and enables efficient communication with the cloud and decreased power consumption at the edge..."
MQTT maintains a persistent connection with the cloud, which is beneficial when signals drop. It buffers data during connectivity issues and synchronises once the connection is restored. Additionally, MQTT offers three Quality of Service (QoS) levels, allowing fleet managers to choose between quick, non-critical messaging and guaranteed delivery for essential data.
CoAP: Designed for Devices with Limited Resources
CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol) is tailored for devices with limited processing power and battery life. Running over UDP, it avoids the overhead of maintaining a persistent connection. Its request-response model is similar to HTTP but consumes far less power, making CoAP a great choice for battery-operated sensors, such as temperature monitors in refrigerated trucks or standalone cargo units in remote areas.
HTTP/HTTPS: Secure Data Exchange for Fleet Systems
HTTP and HTTPS are the go-to protocols for web dashboards and API integration in fleet management systems. While they have a higher overhead compared to MQTT or CoAP, HTTPS is indispensable for secure data exchange. By using TLS/SSL encryption, HTTPS ensures the protection of sensitive fleet data during transmission.
LoRaWAN: Long-Range Monitoring for Remote Areas
LoRaWAN (Long Range Wide Area Network) is a standout option when cellular coverage is unreliable. It can transmit data over distances greater than 15 kilometres, making it ideal for monitoring assets in rural areas. LoRaWAN devices boast impressive battery life, lasting 10–15 years on a single battery, with data rates between 0.3 kbps and 27 kbps.
Olivier Hersent, Chairman & CTO at Actility, explains its practicality:
"With LoRaWAN®, entire cities or countries can be covered with a few base stations, no longer requiring the upfront rollout and maintenance of nodes as in traditional mesh networking"
Using Chirp Spread Spectrum modulation, LoRaWAN can maintain communication even with up to 30% signal interference, making it highly reliable for rural asset tracking.
| Protocol | Transport Layer | Header Size | Battery Life | Range | Best Fleet Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT | TCP | 2 bytes | Moderate | Network dependent | Real-time vehicle telemetry |
| CoAP | UDP | Minimal | Very long | Network dependent | Battery-powered sensors |
| HTTP/HTTPS | TCP | High | Low | Network dependent | Secure dashboards & APIs |
| LoRaWAN | LoRa | Low | 10–15 years | Up to 15 km | Rural asset monitoring |
Each of these protocols serves a distinct purpose, offering tailored solutions for maintaining fleet connectivity across diverse conditions.
How IoT Protocols Work with Fleet Hardware
How Fleet Devices Communicate Using IoT Protocols
Telematics devices serve as the bridge between vehicles and the cloud. These devices gather data from various sensors - such as GPS, fuel levels, engine diagnostics, and driver behaviour - and process it according to the requirements of specific IoT protocols before transmitting it. The telematics unit not only sends this data to the cloud but also receives commands from the platform. These commands could include route updates, configuration adjustments, or even remote engine immobilisation for security purposes. Essentially, IoT protocols establish standardised rules for identifying devices, packaging data, and ensuring it reaches the right destination.
This seamless exchange of data is what enables real-time fleet management. Hardwired telematics units, which are powered continuously, typically use MQTT over 4G/LTE networks for reliable, two-way data transmission. This ensures compliance monitoring and real-time performance tracking. On the other hand, battery-powered trackers are better suited to protocols like LoRaWAN or NB-IoT. These allow devices to operate for over a decade on a single battery. Meanwhile, data-heavy devices such as AI dashcams rely on HTTP/HTTPS over high-speed cellular networks (4G/5G) to manage large video files and advanced computer vision processing.
This communication setup forms the foundation for comparing how these protocols perform in different fleet environments.
Protocol Comparison for Fleet Environments
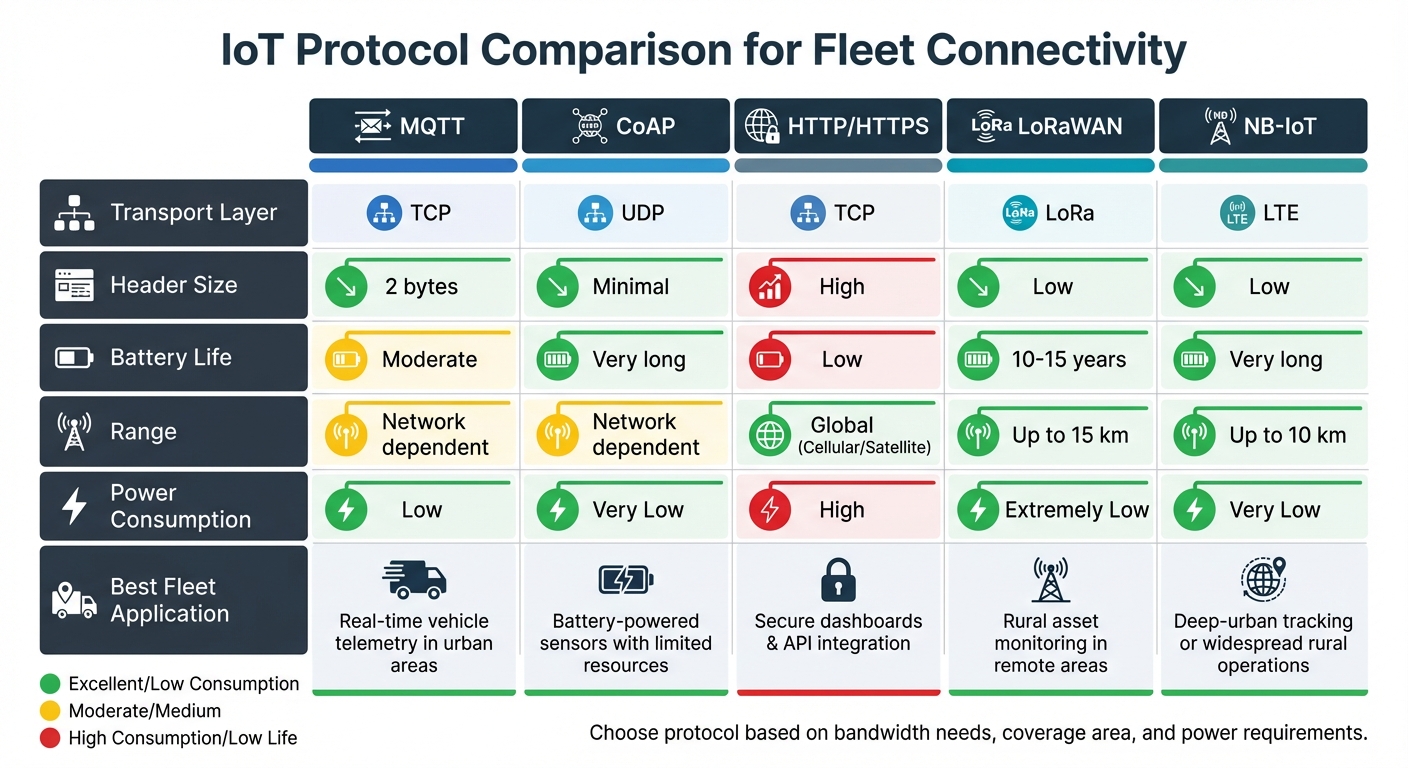
Each IoT protocol is tailored to meet specific operational needs, balancing factors like bandwidth, range, and power consumption. Below is a comparison of how these protocols align with the varied demands of fleet management:
| Protocol | Bandwidth | Range | Power Consumption | UK Fleet Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MQTT | Low | Network-dependent (Cellular/Wi-Fi) | Low | High (Urban): Perfect for real-time telemetry and frequent updates. |
| CoAP | Very Low | Network-dependent | Very Low | High (Constrained): Ideal for battery-powered sensors with limited resources. |
| HTTP/HTTPS | High | Global (via Cellular/Satellite) | High | High: Essential for secure platform integration and web-based dashboards. |
| LoRaWAN | Very Low | Long range (up to 15 km) | Extremely Low | High (Rural): Great for basic monitoring in remote areas. |
| NB-IoT | Low | Long range (up to 10 km) | Very Low | High (National): Excellent for deep-urban tracking or widespread rural operations. |
This comparison highlights how each protocol is best suited for specific fleet scenarios. For urban fleets with strong cellular coverage, MQTT offers the efficiency needed for real-time tracking. In contrast, rural operations benefit from LoRaWAN’s impressive range and low power consumption. For secure platform integration and data-heavy devices, HTTPS remains the go-to choice. Each protocol plays a vital role in ensuring efficient and reliable fleet communication, tailored to the unique challenges of different environments.
How to Implement IoT Protocols in Fleet Management Systems
Step-by-Step Guide to Deploy IoT Protocols
Start by identifying your fleet's goals and the challenges you aim to address - whether it’s reducing fuel consumption, improving safety scores, or ensuring timely deliveries. Clearly define measurable targets. For example, fleets that combine driver coaching with IoT-powered route optimisation have reported fuel savings of 8% to 15%.
Next, consider your data needs. High-bandwidth tasks like video monitoring require different protocols compared to basic GPS tracking. For instance, fleets using AI-powered dashcams might rely on HTTP/HTTPS over 4G/5G networks, while simpler location tracking can use MQTT over LTE.
Evaluate your connectivity environment. For fleets operating in rural or underground areas, long-range, low-power protocols are often the best choice. Multi-carrier SIMs with failover capabilities ensure uninterrupted service, even in remote or cross-border operations.
Select hardware that aligns with your operational requirements. Options include hardwired devices for compliance-heavy workflows, self-install plug-ins for fleets with high turnover, or battery-powered sensors for unpowered assets like trailers.
Set up IoT gateways to convert local sensor data into internet-ready formats. These gateways act as a bridge, translating data from systems like the OBD2/CAN bus into MQTT or HTTP messages for cellular transmission. Ensure your platform supports open APIs to prevent data silos. As Keystone Technology highlights:
"IoT only pays off when it's integrated, not isolated"
Integrating with existing systems like ERP, billing, or maintenance platforms ensures smooth data flow across your operations.
Before full deployment, pilot the system with a small subset of your fleet. This allows you to test performance, return on investment, and the overall architecture. IoTPortal notes:
"most IoT problems are architectural, not product-related"
Use fleet management software to monitor performance, tracking metrics like data transmission, device uptime, and protocol efficiency. With the IoT fleet management market expected to grow from £9.3 billion in 2024 to £33.5 billion by 2034, adopting these technologies is becoming increasingly important.
Once the protocols are in place and operational, shift your focus to implementing strong security measures to protect your system.
Security and Reliability in Protocol Implementation
Security should be a priority at every stage of your IoT deployment. Use HTTPS encryption and multi-factor authentication to secure data transmitted between fleet devices and platforms. Replace default manufacturer passwords with strong, unique 12-character credentials to prevent brute-force attacks. For remote diagnostics and maintenance, adopt a VPN-based access model instead of exposing devices directly to the internet. This reduces the risk of cyberattacks.
For critical operations, consider using dual-tracker systems. GRS Fleet Telematics, for instance, employs this redundancy to ensure connectivity even if one network or device fails - an essential feature for fleets operating in diverse environments, from urban areas to remote regions.
Keep devices up to date by applying firmware updates as soon as they’re available. Kaspersky stresses:
"Software updates are an essential factor in IoT device security. Devices that use out-of-date IoT software are easier for hackers to compromise"
Support over-the-air (OTA) updates to patch vulnerabilities without needing physical vehicle inspections.
To enhance security further, segment your network by isolating IoT devices from your primary organisational systems. This prevents attackers from moving laterally in case of a breach. Disable unused features, such as Bluetooth or unnecessary ports, to minimise potential entry points for attackers. For industries with strict compliance requirements, opt for managed-install devices, which offer better tamper resistance than self-installed units.
Secure IoT protocols not only improve safety but also enhance efficiency. Real-time tracking can cut unauthorised vehicle use by up to 18%, while predictive analytics can reduce unexpected downtime by 25%.
Practical Applications of IoT Protocols in Fleet Operations
Optimising Routes and Fuel Efficiency
Using MQTT, real-time sensor data can be transmitted instantly. For instance, if a driver engages in harsh acceleration or idling for extended periods, alerts are sent directly to fleet managers. This immediate feedback not only improves connectivity but also enables the creation of driver scorecards. These scorecards encourage eco-friendly driving habits, which can significantly reduce fuel consumption.
Meanwhile, CoAP is ideal for battery-powered sensors that monitor trailer conditions, such as temperature or humidity, with minimal energy use. By integrating this data with route optimisation algorithms, fleets can reduce unnecessary mileage and idling time - two key contributors to high fuel costs.
In February 2025, an International Electric Vehicle Company leveraged the Cisco IoT Control Center to enhance fleet connectivity across Europe. By automating rate-plan adjustments, they avoided data overage charges while maintaining real-time tracking capabilities, ultimately cutting monthly per-car network costs by 88%.
These advancements in efficiency also play a pivotal role in bolstering fleet security.
Improving Vehicle Security with IoT Protocols
LoRaWAN excels in providing extended connectivity, particularly in remote areas where cellular coverage is unreliable. For example, if a vehicle crosses a predefined geofence boundary, LoRaWAN-enabled sensors can instantly send alerts, allowing swift action to prevent theft.
GRS Fleet Telematics takes security further with a dual-tracker system. By combining primary cellular tracking with Bluetooth backup, they ensure uninterrupted location monitoring - even if one network fails. This approach has resulted in a 91% recovery rate for stolen vehicles, supported by 24/7 recovery assistance.
Additionally, hardwired tamper-resistant devices offer enhanced protection. Unlike self-installed systems, these devices are more challenging to disable, providing an extra layer of security.
Beyond security, IoT protocols are also transforming fleet maintenance strategies.
Predictive Maintenance and Fleet Diagnostics
HTTPS ensures the secure transmission of diagnostic data from vehicles to cloud platforms. When a vehicle detects a fault, it generates Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) via its OBD2/CAN bus system. These codes are securely sent using HTTPS, enabling fleet management systems to analyse the data and predict potential component failures. This shift to predictive analytics improves maintenance workflows and reduces unexpected breakdowns.
MQTT further enhances predictive maintenance by allowing sensors - such as vibration monitors - to publish data to a central broker. If sensor readings indicate a potential issue, the system sends immediate alerts, enabling proactive repairs before problems escalate. In February 2025, the CEO of an Industrial Monitoring Company highlighted how the Cisco IoT Control Center reduced telematics device testing and deployment time from four days to just five minutes.
Lastly, LwM2M (Lightweight Machine-to-Machine) provides a standardised method for remote firmware updates. This ensures that diagnostic hardware remains up-to-date and secure without requiring physical inspections. By addressing minor issues early, fleets can minimise downtime and avoid costly repairs.
Conclusion
IoT protocols are the backbone of fleet connectivity, ensuring that vehicles, sensors, and platforms can exchange data reliably. This seamless communication enables real-time visibility, predictive maintenance, and strengthens overall security.
"IoT protocols are as critical to the existence of IoT as the things themselves." – Mary K. Pratt
The choice of protocol has a direct impact on operational efficiency. Lightweight options like MQTT and CoAP reduce network strain and extend device battery life. When combined with low-power wide-area network technologies, some devices can operate for over a decade on a single battery. For extended coverage, LoRaWAN excels, offering ranges of up to 30 km in specific conditions - ideal for areas where traditional cellular networks falter.
Security is a top priority, especially with the fleet management systems market expected to reach 25 million units by 2026. Protocols incorporating TLS encryption and authentication protect sensitive vehicle data from cyber threats. For example, GRS Fleet Telematics employs dual-tracker systems using both cellular and Bluetooth technologies, achieving an impressive 91% recovery rate for stolen vehicles. These plans start at just £7.99 per month. Such robust security measures not only safeguard data but also enhance fleet reliability.
FAQs
What should I consider when choosing the best IoT protocol for my fleet?
Choosing the best IoT protocol for your fleet involves weighing several factors, such as your operational goals, the type of data you need to transmit, and the conditions under which your fleet operates. Critical aspects to consider include power efficiency, transmission range, security, and whether you need real-time communication.
For instance, WiFi and Bluetooth are excellent choices for short-range, high-bandwidth needs. On the other hand, if your priority is long-range tracking with low power consumption, low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN) like LoRaWAN or NB-IoT are more suitable. For fleets that depend on real-time updates - like vehicle tracking or telematics - you'll require a protocol that guarantees fast and steady connectivity.
To ensure your fleet's connectivity is as efficient as possible, assess your specific requirements carefully and select a protocol that offers the right balance of reliability, scalability, and security. Providers like GRS Fleet Telematics offer solutions designed to integrate seamlessly and deliver dependable performance tailored to your business operations.
What security measures should you take when using IoT protocols in fleet management?
When incorporating IoT protocols into fleet management, security plays a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of your systems. One of the most effective steps is using encrypted communication channels. This ensures that data transmitted between vehicles, devices, and servers stays secure and cannot be intercepted or tampered with.
Another essential measure is implementing device authentication and access controls. This restricts network access to only authorised users and devices, reducing the risk of unauthorised intrusions. Keeping IoT devices and software up to date is equally important, as regular updates help address vulnerabilities. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems can detect suspicious activity or potential breaches, allowing swift action to mitigate risks.
By prioritising these security practices, businesses can significantly reduce cybersecurity threats, keeping their fleets protected and their operations running efficiently across the UK.
How do IoT protocols help improve fleet maintenance and minimise downtime?
IoT protocols are essential for keeping fleets in top condition and cutting down on downtime. They enable real-time communication between vehicles and management systems, allowing telematics devices to track critical metrics like engine health, brake performance, and fuel efficiency. This means potential issues can be spotted early, giving fleet operators the chance to address them before they turn into costly breakdowns.
With cloud-based systems in the mix, IoT protocols take things a step further by offering real-time data analysis. Instead of sticking to rigid maintenance schedules, fleet managers can base decisions on the actual condition of each vehicle. This approach trims unnecessary maintenance costs, keeps expenses in check, and ensures vehicles spend more time on the road. Plus, reliable connectivity - even in remote areas - guarantees a steady flow of data, boosting operational efficiency and maximising fleet availability. For businesses across the UK, these IoT-enabled systems translate into cost savings and smoother fleet operations.




