How EV Telematics Predicts Charging Station Demand
Telematics uses vehicle location, battery and energy data to forecast EV charging demand, optimise station placement and cut fleet energy costs.

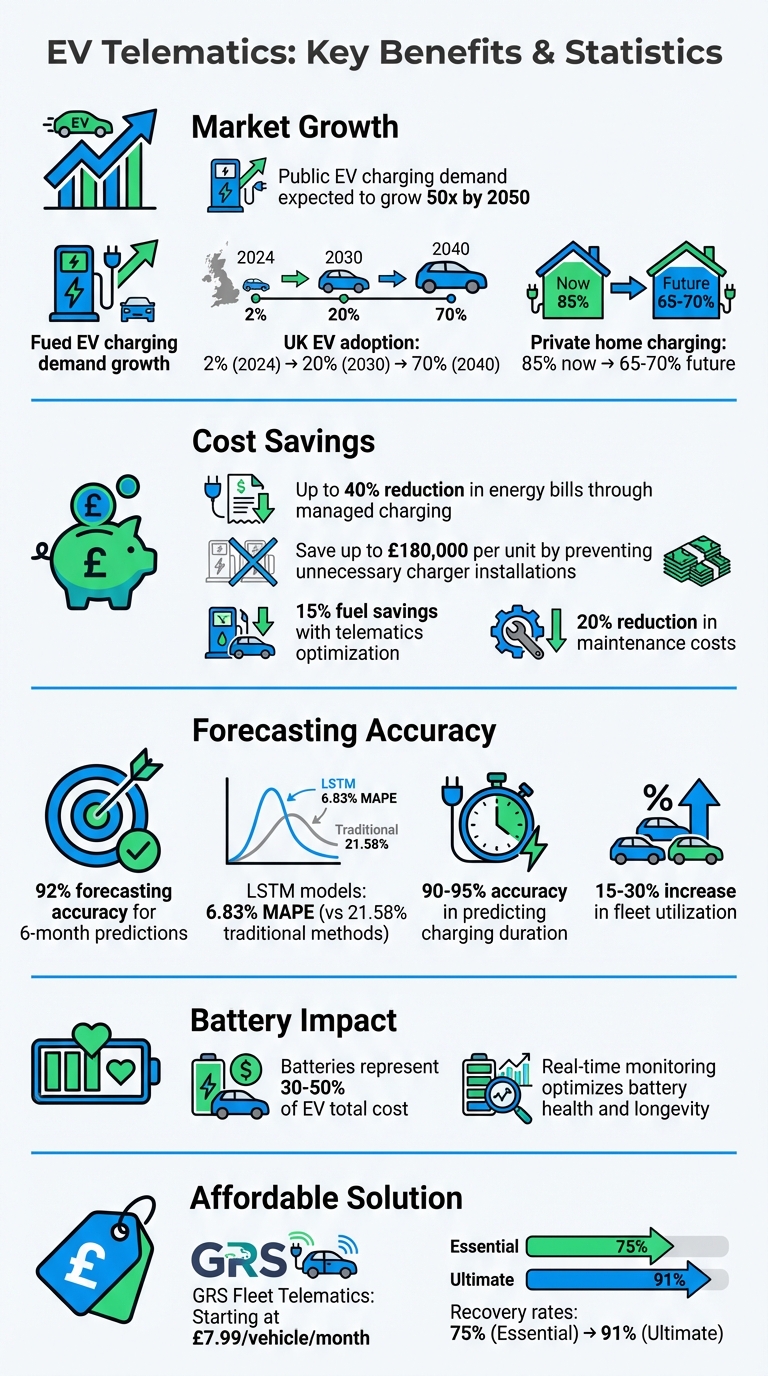
EV telematics helps fleet managers predict charging station demand by using data from vehicles like location, battery status, and energy usage. This technology analyses patterns to optimise charging schedules, reduce costs, and guide where new stations should be built. With EV adoption increasing and public charging demand expected to grow 50 times by 2050, telematics-driven forecasting is key for efficient fleet operations and infrastructure planning.
Key takeaways:
- Cost Savings: Managed charging can cut energy bills by up to 40% by using off-peak electricity rates.
- Infrastructure Optimisation: Predictive models prevent unnecessary charger installations, saving up to £180,000 per unit.
- Data-Driven Insights: Metrics such as battery health, trip chains, and charging patterns guide decision-making.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Live data refines predictions and helps adjust to changing conditions.
Fleet operators can use systems like GRS Fleet Telematics to access these insights, starting at £7.99 per vehicle monthly. This ensures better planning, lower costs, and improved fleet performance.
EV Telematics Benefits: Cost Savings and Forecasting Accuracy Statistics
Exploring Telematics - a data driven approach to EV fleets
Collecting and Analysing EV Telematics Data
Telematics data is gathered using an OBD II/CAN-BUS device, which connects directly to the vehicle’s OBD II or CAN-BUS port. This device uses GPS for location tracking and a SIM card to send data over cellular networks to cloud-based fleet management systems. The data collected includes standard metrics like GPS location, odometer readings, and vehicle speed, alongside EV-specific details such as battery state of charge (SoC), state of health (SoH), energy consumption rates, battery voltage, current, and temperature.
This high-frequency data plays a critical role in refining digital twin models, enabling precise monitoring of battery performance. This is particularly important as batteries represent 30–50% of an EV’s total cost. Fleet managers use integrated dashboards to keep track of these metrics, helping them optimise energy efficiency and plan recharging schedules. The continuous flow of data also allows for the identification of charging events and other essential fleet metrics.
Key Data Sources in EV Telematics
Within this data flow, several key sources stand out for defining charging events and assessing vehicle performance. Charging events, for instance, are identified when the vehicle remains stationary (verified by GPS), energy consumption drops to low or negative levels, and battery charge increases.
"My starting point is usually the telematics fleet management systems where trucks send data while driving. The vehicles are equipped with numerous different sensors that daily send a lot of data." – Maja Feierabend, Data Scientist, Volvo Group
The core telematics data includes real-time GPS tracking, trip distances, idling times, and stop durations. For EV-specific insights, metrics like battery voltage, current draw, temperature, SoC, and SoH are crucial. Fleet operators also monitor parameters such as arrival and departure times, the difference between initial and target SoC levels, battery capacity, and energy consumption rates (measured as delta energy over delta time). Additionally, historical charging patterns and "trip chains" - the sequence of trips between charging sessions - offer valuable inputs for predictive modelling.
Factors That Influence Charging Demand
The detailed metrics collected help build models that forecast charging demand based on various factors like time, weather, and usage patterns. Time of day significantly influences charging behaviour, with peak demand aligning with rush hours and minimal activity occurring overnight. Weekday charging typically spikes before and after work hours, while weekend demand is steadier, often peaking between 10 AM and 4 PM.
Seasonal shifts and weather conditions also play a role, as they can impact driving range and battery efficiency. Traffic patterns further affect journey times and energy use. The type of charging station also matters - whether it’s a 95 kW rapid charger or a 150 kW ultra-fast unit - as this determines how long a vehicle occupies a charging point.
With EV adoption in the UK expected to grow from about 2% in 2024 to a projected 20% by 2030 and 70% by 2040, these trends are likely to become more pronounced. Fleet operators must also prepare for a shift in charging habits. Currently, around 85% of EV users rely on private home charging, but this is forecast to drop to 65–70% as more drivers without off-street parking begin using public charging facilities.
Using Predictive Models for Demand Forecasting
Predictive models have become essential tools for forecasting charging demand, leveraging the wealth of data collected through telematics. By analysing both historical trends and live data, machine learning algorithms can anticipate when and where demand will surge. This allows fleet operators to manage resources more effectively and minimise disruptions.
Time-Series Forecasting with Machine Learning
Machine learning techniques like Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks are particularly adept at recognising sequential patterns in data. For instance, a January 2018 study used an LSTM model trained on data from 76,000 electric vehicles (EVs) in Beijing to predict station-level demand over a one- to five-hour period. The results were impressive, with the model achieving a Mean Absolute Percentage Error (MAPE) of just 6.83%. This performance far surpassed that of traditional ARIMA models (21.58% MAPE) and multilayer perceptron (MLP) networks (18.31% MAPE).
Temporal Fusion Transformers (TFT) take this a step further by combining LSTM layers with static variables, such as connector type, battery capacity, and ambient temperature. Between November 2021 and July 2024, a deep learning system trained on over 909,000 real-world DC fast-charging sessions across northwestern Europe demonstrated exceptional accuracy. It achieved 90% accuracy in predicting charging duration from a single data point on the power-to-SoC profile. This accuracy increased to 95%, with an absolute error of less than one minute, when six data points were analysed within the first five minutes of a session.
"The LSTM model outperformed the ARIMA, and MLP models, and their MAPE values are 6.83%, 21.58%, and 18.31%, respectively." – Shengyou Wang et al., Applied Energy
Combining Location and Behaviour Data
To further refine demand forecasts, integrating spatial and behavioural data is key. For example, combining user behaviour patterns with location-based clustering can significantly improve prediction accuracy. Knowing whether a vehicle is charging overnight, for instance, can reduce the MAPE of duration predictions from over 200% to just 15%. Additionally, models that consider the proximity of neighbouring stations can identify shared occupancy trends, enhancing forecasting precision.
A study conducted from March to April 2023 in central Wuhan, China, analysed operational data from five charging stations, encompassing 123 fast-charging piles. By incorporating factors like occupancy rates, time-of-day indices, and electricity price correlations into an "Attention-SLSTM" model, researchers achieved a MAPE of 9.768% for station-level demand forecasting. The study also found that the first two current states (t-1 and t-2) were the most reliable predictors for short-term occupancy. Fleet operators can adopt similar approaches by integrating historical data, pricing trends, and real-time session updates to continuously enhance the precision of their predictions as new data becomes available.
Optimising Charging Station Placement and Operations
Once predictive models identify demand patterns, the next step is turning those insights into effective infrastructure decisions. Telematics data not only predicts when charging will happen but also pinpoints where stations should be located and how they can operate to ensure better efficiency and usage.
Using Data to Decide Station Locations
Choosing the best spots for charging stations means weighing factors like consumer demand, electricity grid capacity, and financial feasibility. Telematics systems merge vehicle journey data with geospatial details - such as population movement, property types, and Distribution Network Operator (DNO) capacity maps - to identify areas suited for high-power chargers. As the UK’s Geospatial Commission highlights, "the location of where chargepoints are installed is as important as the number installed".
A three-year trial using data from private hire vehicle (PHV) journeys successfully matched charging demand with substation capacities, giving DNOs a practical way to handle the growing number of EVs while reducing strain on the grid.
Fleet operators should focus on areas where residents don’t have off-street parking, as these individuals depend more on public charging. While over 85% of current EV owners have private parking, this figure is expected to drop to between 65% and 70% as EV adoption grows. Tools like spatial analysis software and property databases, such as OS AddressBase, can help identify these critical locations. While strategic placement hinges on data integration, keeping operations efficient requires ongoing monitoring.
Adapting to Demand with Real-Time Monitoring
Static planning isn’t enough - telematics systems that monitor in real time can refine predictions and adjust to changing conditions. By tracking factors like vehicle standstill (via GPS), low power consumption, and increases in State of Charge, telematics can pinpoint charging events and allocate power more effectively.
Fleet operators in the UK can combine vehicle telematics with charging management systems to scale operations smartly and determine the best times for infrastructure expansion based on actual energy use and route patterns. Dynamic scheduling, which takes into account Time-of-Use (TOU) electricity rates, battery wear and tear, and user satisfaction, helps cut costs while improving service quality.
For short-term occupancy predictions, using real-time data on how long a charging point has already been in use can make forecasts much more accurate. When applying ensemble models like Random Forest, operators should exclude predictions shorter than the time a charger has already been occupied and rely on the median of the remaining results. Pairing these predictions with live traffic data ensures demand forecasts stay reliable, even during unexpected spikes or disruptions.
Deploying Telematics Solutions with GRS Fleet Telematics

When demand forecasting is in place, implementing advanced telematics systems becomes a key step in streamlining fleet operations.
GRS Fleet Telematics Features for EV Management
GRS Fleet Telematics provides a robust digital platform designed to support fleet electrification. By combining real-time tracking with AI-powered analytics, it helps predict fleet requirements with impressive accuracy. The system’s dual-tracker technology ensures uninterrupted data collection, even in tough conditions, offering the precision needed for reliable demand forecasting.
The platform gathers data on vehicle location, speed, and route history, which is then processed through machine learning algorithms to uncover trends and anticipate future needs. It also includes predictive maintenance tools that monitor battery health and vehicle performance, ensuring fleets remain operational during busy periods. Custom dashboards allow managers to oversee energy usage, fuel efficiency, and driver behaviour, providing a comprehensive view of fleet performance.
"Data analytics transforms real-time telematics and sensor data into actionable insights that help improve efficiency, reduce costs and enhance safety." – GRS Fleet Telematics
According to GRS Fleet Telematics, these tools can lead to substantial benefits, including up to 15% fuel savings, a 20% reduction in maintenance costs, 92% forecasting accuracy for six months ahead, and a 15–30% increase in fleet utilisation.
Affordable Solutions for Fleet Operators
GRS Fleet Telematics offers cost-effective packages tailored to fleets of all sizes, making advanced telematics accessible.
- Essential Package: For £35 hardware and £7.99 per month, this option provides wired tracking with a 75% recovery rate.
- Enhanced Package: At £79 hardware and £7.99 per month, it adds dual-tracker technology, boosting the recovery rate to 85%.
- Ultimate Package: Priced at £99 hardware and £7.99 per month, this package includes full remote immobilisation, achieving a 91% recovery rate and reducing data loss risks.
Each package includes a monthly subscription covering SIM and data, an account manager, and full platform access. Starting at just £7.99 per vehicle each month, fleet operators gain access to powerful demand forecasting tools. The system also integrates with ERP systems and maintenance records, allowing operators to centralise data, plan maintenance during quieter periods, and monitor driver habits. This insight helps identify inefficiencies like harsh braking or idling, which can waste energy and drive up costs.
Conclusion
EV telematics plays a crucial role in predicting charging demand and streamlining fleet operations. By leveraging real-time data alongside historical trends, these systems enable fleet managers to pinpoint the best charging locations, minimise energy expenses through off-peak scheduling, and extend battery life with predictive maintenance. With public EV charging energy demand expected to surge 50-fold between 2023 and 2050, the ability to anticipate and adapt to charging needs will become increasingly important. These predictive capabilities translate into practical strategies that improve fleet management.
For fleet operators, this technology addresses everyday challenges by simplifying charging management, cutting costs, and boosting fleet dependability.
GRS Fleet Telematics builds on these advancements with a comprehensive solution that integrates seamlessly into fleet operations. Using sophisticated predictive models that combine real-time and historical data, the platform equips fleet managers to plan charging infrastructure and refine operational strategies with confidence.
Starting at just £7.99 per vehicle each month, GRS Fleet Telematics offers demand forecasting while integrating effortlessly with existing systems. It provides the control and visibility needed to scale fleet electrification efficiently, reduce costs, and enhance overall performance.
FAQs
How does EV telematics help reduce fleet energy costs?
EV telematics offers a smart way to lower fleet energy costs by using real-time data to fine-tune charging and driving strategies. By monitoring key factors like vehicle location, speed, battery levels, and routes, it can pinpoint the most cost-effective times and places to charge. Often, this means aligning charging schedules with off-peak electricity tariffs, helping fleets dodge higher costs during peak periods. In some cases, it can even take advantage of times when electricity prices dip significantly.
Beyond charging, telematics also evaluates driving habits such as acceleration, braking, and idling. With this information, it suggests smoother driving techniques and more efficient routes, cutting down on energy consumption per kilometre. Advanced AI tools add another layer of efficiency by balancing energy use across the fleet. For instance, vehicles can be rerouted to less crowded charging points or have their charging times shifted to periods of lower demand. These measures not only save money but also help extend the lifespan of batteries, with many UK fleets seeing a 10–20% reduction in total energy costs when using a robust telematics system.
How does machine learning help predict demand at EV charging stations?
Machine learning is central to analysing EV telematics data, offering a way to forecast demand for charging stations. By examining patterns in vehicle usage, travel routes, and charging behaviours, these algorithms can anticipate the times and locations where charging stations will see the most demand.
This predictive insight enables fleet operators to streamline charging schedules, minimise downtime, and enhance operational efficiency. Additionally, it aids in planning charging infrastructure more effectively, ensuring stations are available exactly where they’re needed most.
How can fleet operators use telematics to identify the best locations for EV charging stations?
Fleet operators can tap into EV telematics data - like GPS routes, dwell times, battery state-of-charge (SOC), and energy consumption - to figure out where charging demand is highest. By studying fleet patterns, such as frequent stops in particular areas or routes passing through regions with limited charging infrastructure, they can identify the best spots for new charging stations.
This process generally unfolds in three stages. First, telematics systems, such as GRS Fleet Telematics, organise raw data into a format that's easy to work with. Next, analytical tools merge this data with external factors, like local grid capacity and the locations of existing chargers, to create a detailed demand map. Finally, practical considerations - such as parking availability and how close the site is to depots - are factored in to pinpoint the most suitable locations. By using this data-driven strategy, operators can position charging stations where they’ll have the greatest impact, enhancing fleet performance and easing drivers’ concerns about range.




